 DeepBio得分:
DeepBio得分:
 DeepBio得分
是基于文獻引用次數,影響因子,文獻新近度等因素計算的客觀產品評級,得分越高表明該產品經過越可靠的實驗驗證,質量可信度越高
DeepBio得分
是基于文獻引用次數,影響因子,文獻新近度等因素計算的客觀產品評級,得分越高表明該產品經過越可靠的實驗驗證,質量可信度越高
|
2家供應商在售
|
||||||
| 商品名稱 | 規格 | 代理級別 | 價格 | 運費 | 供應商 | 購買 |
|
Neurofilament-L (DA2) Mouse mAb
交貨周期:現貨
|
20 μl | 經銷 |
登錄可見
|
- |
北京敏泰元科技有限公司 |
庫存:20
|
|
CST 2835T Neurofilament-L(DA2) Mouse mAb
交貨周期:部分現貨,期貨3-4周左右,優質售后
|
20μl | 經銷 |
登錄可見
|
- |
上海優寧維生物科技股份有限公司 |
庫存:999
|
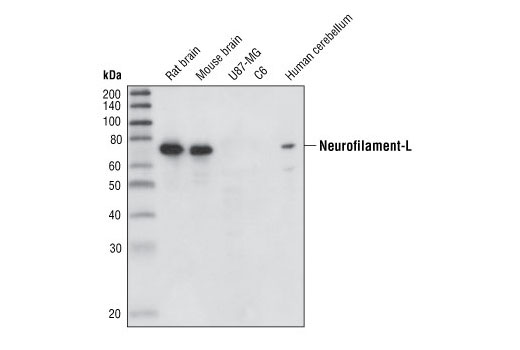
| REACTIVITY | H M R |
| SENSITIVITY | Endogenous |
| MW (kDa) | 70 |
| Source/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) | 1:50 |
| Immunofluorescence (Frozen) | 1:100 |
Supplied in 10 mM sodium HEPES (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 100 μg/ml BSA, 50% glycerol and less than 0.02% sodium azide. Store at –20°C. Do not aliquot the antibody.
Neurofilament-L (DA2) Mouse mAb detects endogenous levels of total Neurofilament-L protein. This antibody does not stain Neurofilament-L in cultured human cells by immunofluorescence and is recommended for rodent tissues only.
Human, Mouse, Rat
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with purified and enzymatically dephosphorylated pig neurofilament, light chain.
The cytoskeleton consists of three types of cytosolic fibers: actin microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Neurofilaments are the major intermediate filaments found in neurons and consist of light (NFL), medium (NFM), and heavy (NFH) subunits (1). Similar in structure to other intermediate filament proteins, neurofilaments have a globular amino-terminal head, a central α-helical rod domain, and a carboxy-terminal tail. A heterotetrameric unit (NFL-NFM and NFL-NFH) forms a protofilament, with eight protofilaments comprising the typical 10 nm intermediate filament (2). While neurofilaments are critical for radial axon growth and determine axon caliber, microtubules are involved in axon elongation. PKA phosphorylates the head domain of NFL and NFM to inhibit neurofilament assembly (3,4). Research studies have shown neurofilament accumulations in many human neurological disorders including Parkinson's disease (in Lewy bodies along with α-synuclein), Alzheimer's disease, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) (1).
 京公網安備 11010802025067號 增值電信業務經營許可證:京B2-20171454 ICP備案號:京ICP備16050672號-1
喀斯瑪科技版權所有 2017-
京公網安備 11010802025067號 增值電信業務經營許可證:京B2-20171454 ICP備案號:京ICP備16050672號-1
喀斯瑪科技版權所有 2017-

![]() 藥品醫療器械網絡信息服務備案: (京)-網藥械信息備字(2022)第00393號
醫療器械網絡交易服務第三方平臺備案編號:京網械平臺備字(2021)第00006號
藥品醫療器械網絡信息服務備案: (京)-網藥械信息備字(2022)第00393號
醫療器械網絡交易服務第三方平臺備案編號:京網械平臺備字(2021)第00006號